The Dialogue System consists of these main parts:
A dialogue database is an asset file that contains your conversations, quests, and user-defined variables. You will typically use the Dialogue Editor to edit its content, although you can also import from several others formats.
The dialogue database contains design-time content, fields that you edit in the Unity editor. At runtime, the Dialogue System treats the dialogue database as read-only; it loads the dialogue database fields into Lua where the values can be changed during play.
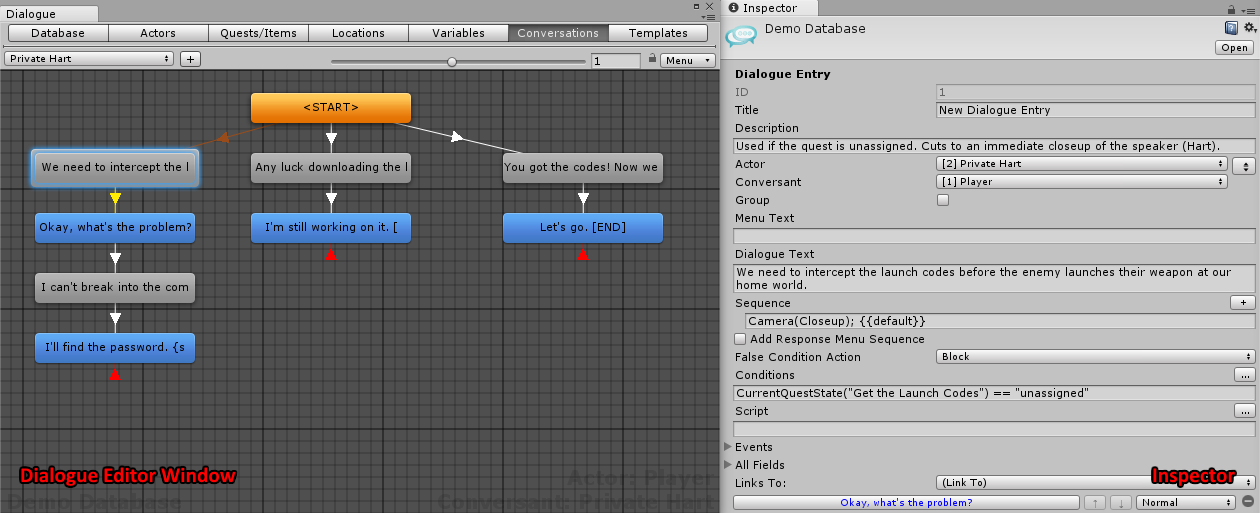
Use the Dialogue Editor to edit your dialogue database and view its runtime state in play mode. For detailed information about the Dialogue Editor, see Dialogue Editor. To import other formats such as articy:draft and Chat Mapper, see Import & Export.
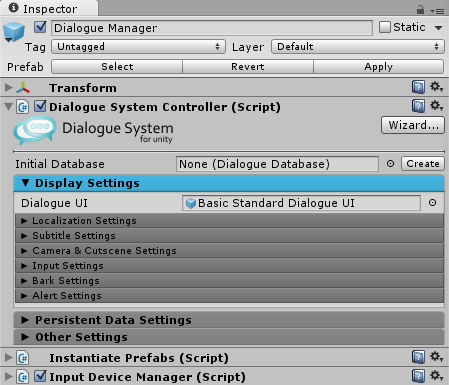
The Dialogue Manager is a GameObject in your scene that coordinates all Dialogue System activity and holds the Dialogue System’s runtime data. The Dialogue Manager section covers it in detail.

The Dialogue System uses the following UIs:
For detailed information about dialogue UIs, see Dialogue UIs. For information about quest UIs, see Quests.
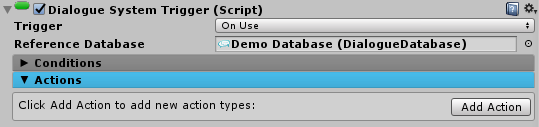
The Dialogue System provides components to interact with GameObjects and perform actions such as starting conversations and updating quest states.
The Dialogue System supports localization of dialogue database content and general UI elements. For information about localization, see Localization.
While the Dialogue System’s default capabilities are quite powerful and flexible, you can also create your own logic functions, cutscene actions, UI types, and more. This is covered in Scripting.
<< Demo Scene | Quick Start >>